Self-assembled oligomeric procyanidin–insulin hybrid nanoparticles: a novel strategy for controllable insulin delivery†
Abstract
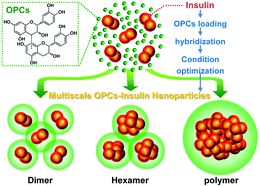
Natural oligomeric procyanidin (OPC) with high biological and pharmacological activities was successfully used to synthesize OPC–insulin (OPC–

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...