Electrospinning and additive manufacturing: converging technologies
Abstract
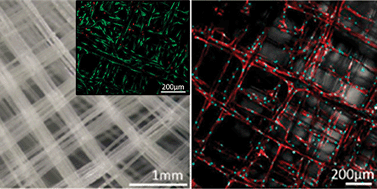
A well-engineered scaffold for regenerative medicine, which is suitable to be translated from the bench to the bedside, combines inspired design, technical innovation and precise craftsmanship.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...