Synthesis of modified chitosan-based molecularly imprinted polymers for adsorptive protein separation
Abstract
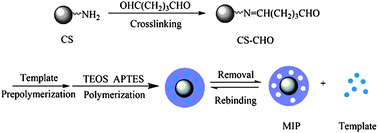
A simple molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was prepared to recognize the template lysozyme (Lys). Chitosan (CS) was selected as the functional biopolymer to enhance the adsorption capacity. The aldehyde group was introduced to CS, so that the template protein could be immobilized onto the modified CS beads. After the template protein was successfully immobilized, two kinds of organic siloxane, tetraethoxysiloxane (TEOS) and 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane (APTES), were added and polymerized via a sol–gel process in aqueous solution at 25 °C. After template removal, adsorption experiments were performed to study the properties of the synthesized MIP. The results showed that the MIP exhibited much higher adsorption capacity for Lys than the non-imprinted polymer (NIP). The theoretical maximum adsorption capacity (Qmax) and equilibrium constant (KL) were determined by the Langmuir model, which turned out to be 15.89 mg g−1 and 6.78. The selectivity of the MIP was verified by direct adsorption of a single reference protein and mixed protein. The UV measurement and sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis results showed the MIP had a relatively high adsorption capacity and excellent selectivity, which made it possible to remove the template protein from different sample solutions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...