Characterization of volatile components in Calligonum comosum by coupling gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and mean field approach independent component analysis
Abstract
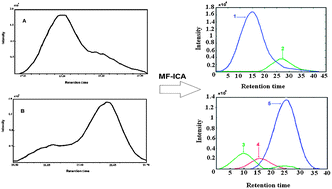
The volatile components of Calligonum comosum were extracted using a simultaneous distillation extraction (SDE) method and were analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The mass spectra obtained from their components were surveyed by searching in NIST and Wiley libraries, but some of the components did not show a satisfactory matching percentage. Morphological score (MS) has used for chemical rank determination, and simple-to use interactive self-modeling mixture analysis (SIMPLISMA) was used as an initial estimate in the iterative process. In the next step, the overlapping peaks were resolved into pure chromatograms and mass spectra using independent component analysis (ICA) methods. Among different independent component analysis algorithms, mean field (MF) applying non-negativity constraints on concentration and spectra profiles is used in this research. MF-ICA can be used as an alternative method for a rapid and accurate analysis of real, multi-component, challenging systems such as essential oils. The resolved mass spectra were satisfactorily identified using mass spectral searches in NIST and Wiley libraries. The consequences of this study show that joining of hyphenated chromatographic methods and resolution techniques provide a satisfactory method for precise analysis of essential oils along with expanding the number of constituents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...