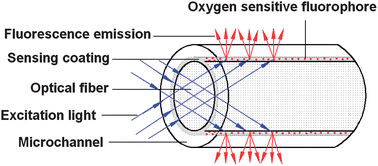
A novel integrated fiber-optic sensor with micro detection volume is developed and evaluated for O2 determination on a breath-by-breath basis in human health monitoring applications. The sensing element was fabricated by dip-coating an uncladded optical fiber with [Ir(piq)2(acac)]-doped hybrid fluorinated ORMOSIL (organically modified silicate) film, which was prepared from 3,3,3-trifluoropropyltrimethoxysilane (TFP-TriMOS) and n-propyltrimethoxysilane (n-propyl-TriMOS). The sensor was then constructed by inserting the prepared optical fiber into a transparent capillary. A microchannel formed between the optical fiber and the capillary inner wall acted as a flow cell for the sample flowing through. The evanescent wave (EW) field produced on the fiber core surface can excite the O2-sensitive fluorophores of [Ir(piq)2(acac)] to produce emission fluorescence. O2 can be sensed by its quenching effect on the emission fluorescence intensity. Spectroscopic properties have been characterized by FTIR and fluorescence measurements. Stern–Volmer and Demas models were both employed to analyse the sensor sensitivity, which is 13.0 with the LOD = 0.009% (3σ) and the response time is about 1 s. By integrating the sensing and detection elements on the optical fiber, the novel configuration showed advantages of easy fabrication and low cost. Parameters of sensitivity, response time, repeatability, humidity effect and temperature effect were discussed in detail. The proposed sensor showed potential for practical in-breath O2 analysis application due to its advantages of easy fabrication, low cost, fast response, excellent hydrophobicity, negligible temperature interference and suitable sensitivity.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...