Cyanide SERS as a platform for detection of volatile organic compounds and hazardous transition metal ions
Abstract
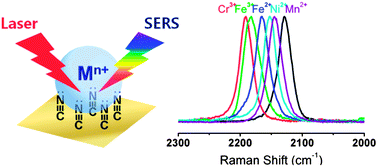
It is demonstrated herein that cyanide adsorbed on nanostructured Au is a very useful system for the detection of not only volatile organic compounds (VOCs) but also transition metal ions by means of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...