Copper@carbon coaxial nanowires synthesized by hydrothermal carbonization process from electroplating wastewater and their use as an enzyme-free glucose sensor†
Abstract
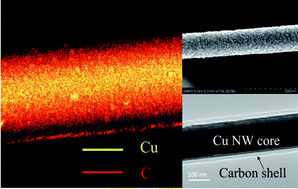
In the pursuit of electrocatalysts with great economic and ecological values for non-enzymatic glucose sensors, one-dimensional copper@carbon (Cu@C) core–shell coaxial nanowires (NWs) have been successfully prepared via a simple continuous flow wet-chemistry approach from electroplating wastewater. The as-obtained products were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, selected area electron diffraction, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy. The electrocatalytic activity of the modified electrodes by Cu@C NWs towards glucose oxidation was investigated by cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry. It was found that the as-obtained Cu@C NWs showed good electrochemical properties and could be used as an electrochemical sensor for the detection of glucose molecules. Compared to the other electrodes including the bare Nafion/glassy carbon electrode (GCE) and several hot hybrid nanostructures modified GCE, a substantial decrease in the overvoltage of the glucose oxidation was observed at the Cu@C NWs electrodes with oxidation starting at ca. 0.20 V vs. Ag/AgCl (3 M KCl). At an applied potential of 0.65 V, Cu@C NWs electrodes had a high and reproducible sensitivity of 437.8 µA cm−2 mM−1 to glucose. Linear responses were obtained with a detection limit of 50 nM. More importantly, the proposed electrode also had good stability, high resistance against poisoning by chloride ion and commonly interfering species. These good analytical performances make Cu@C NWs promising for the future development of enzyme-free glucose sensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...