Degradable emulsion-templated scaffolds for tissue engineering from thiol–ene photopolymerisation†
Abstract
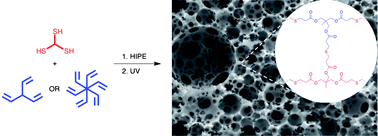
Emulsion templating has been used to prepare highly porous polyHIPE materials by thiol–ene photoinitiated network formation. Commercially available multifunctional thiols and acrylates were formulated into water-in-oil high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) using an appropriate surfactant, and the HIPEs were photo-cured. The temperature of the HIPE aqueous phase was found to influence the morphology of the resulting materials. In agreement with previous work, a higher aqueous phase temperature (80 °C) gave rise to a larger mean void and interconnect diameter. The influence of temperature on morphology was found to be reduced at higher porosity, but still significant. The Young's modulus of the porous materials was shown to be related to the functionality of the acrylate comonomer used. A mixture of penta- and hexa-acrylate gave rise to a 100-fold increase in modulus, compared to an analogous tri-functional acrylate. The materials could be functionalised conveniently by addition of mono-acrylates or thiols to the organic phase of the precursor HIPE. Degradation was observed to occur at a rate depending on the degradation conditions. Under cell culture conditions at 37 °C, 19% mass loss occurred over 15 weeks. The scaffolds were found to be capable of supporting the growth of keratinocytic cells (HaCaTs) over 11 days in culture. Some penetrative in-growth of the cells into the scaffold was observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...