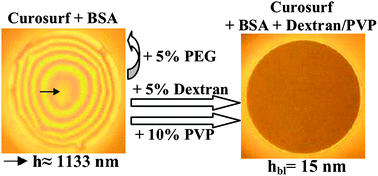
In Adult and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) the concentration of albumin in the alveolar fluid reaches 25–100 mg ml−1. Due to its high adsorption rate albumin adsorbs at the air/water interface making it inaccessible for the lung surfactant (LS). LS inactivation can be prevented by hydrophilic polymers due to depletion attraction osmotic pressure or other specific action. Two commercially available lung surfactant preparations, LSP (Curosurf and Survanta), and four hydrophilic polymers (PEG, dextran, PVP, hyaluronic acid-HA) were investigated in control experiments at one (monolayer) and two interacting air/solution interfaces (foam film) under albumin free and albumin inactivated conditions. The established procedure to measure the minimal surface tension in successive compression–expansion cycles of monolayers revealed that minimal surface tension ≤10 mN m−1 for Survanta is achieved with PEG, PVP, and HA, while for Curosurf with dextran, PVP, and HA. This correlates with the observations of Lu et al., 2005. Foam film experiments with the microinterferometric method of Scheludko and Exerowa revealed the relative ability of the polymers to decrease the effect of albumin inhibition in restoring the formation of stable and homogeneous black films (thickness <17 nm). Stable black foam films are formed by Survanta with PEG, PVP, and HA, while by Curosurf with dextran, PVP, and HA. Kinetic data of Curosurf foam film thinning were interpreted to obtain values of the disjoining pressure. An interesting change from repulsion to attraction was observed at a thickness of appr. 100 nm. It may be explained by depletion attraction overcoming the steric repulsion. The magnitude of the depletion attraction was estimated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...