Insertion mechanism of cell-penetrating peptides into supported phospholipid membranes revealed by X-ray and neutron reflection†
Abstract
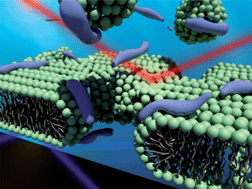
X-Ray and neutron reflectivity measurements on systems composed of a 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) bilayer and transcription-activating-factor derived peptides (TDPs) have allowed us to determine the mechanism of membrane translocation. By monitoring the structural changes of the bilayers caused by the binding of TDPs while systemically varying temperature and TDP concentration, our results revealed the detailed molecular structures of the stepwise interactions that occurred during the translocation of TDP across the lipid bilayers. While little indication of membrane perturbation was observed at low TDP concentrations, we found that the TDP movement across the membrane induced defect formations in the membrane at higher TDP concentrations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...