Adhesion mechanism in a DOPA-deficient foot protein from green mussels†
Abstract
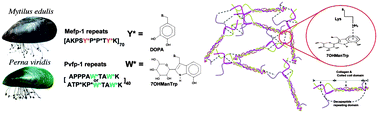
The holdfast or byssus of Asian green mussels, Perna viridis, contains a foot protein, pvfp-1, that differs in two respects from all other known adhesive mussel foot proteins (mfp): (1) instead of the hallmark L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) residues in mfp-1, for example, pvfp-1 contains C2-mannosyl-7-hydroxytryptophan (Man7OHTrp). (2) In addition, pvfp-1 chains are not monomeric like mfp-1 but trimerized by collagen and coiled-coil domains near the carboxy terminus after a typical domain of tandemly repeated decapeptides. Here, the contribution of these peculiarities to adhesion was examined using a surface forces apparatus (SFA). Unlike previously studied mfp-1s, pvfp-1 showed significant adhesion to mica and, in symmetric pvfp-1 films, substantial cohesive interactions were present at pH 5.5. The role of Man7OHTrp in adhesion is not clear, and a DOPA-like role for Man7OHTrp in metal complexation (e.g., Cu2+, Fe3+) was not observed. Instead, cation–π interactions with low desolvation penalty between Man7OHTrp and lysyl side chains and conformational changes (raveling and unraveling of collagen helix and coiled-coil domains) are the best explanations for the strong adhesion between pvfp-1 monomolecular films. The strong adhesion mechanism induced by cation–π interactions and conformational changes in pvfp-1 provides new insights for the development of biomimetic underwater adhesives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...