Amplified optical aptasensors through the endonuclease-stimulated regeneration of the analyte†
Abstract
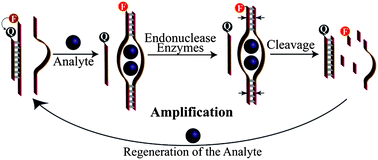
A versatile amplified aptamer-based sensing platform is introduced. The method is based on the design of two subunits of the aptamer sequence corresponding to the respective substrate. Each of the subunits is elongated at its 3′ and 5′ ends with complementary sequences that are cleavable in their duplex structures by the endonucleases, PvuII and HaeIII, respectively. One of the subunits is functionalized by a fluorophore, F, and the subunit is blocked through hybridization to a quencher, Q, modified nucleic acid. Blocking of the aptamer subunit prohibits the formation of the aptamer subunit complex, and it leads to the quenching of the fluorophore. In the presence of the target analyte, the blocked aptamer subunit is separated, and the respective aptamer subunits–analyte complex is formed. The endonucleases PvuII and HaeIII cleave the co-stabilizing duplex regions of the aptamer–analyte complex, leading to the separation of the aptamer–substrate complex, the regeneration of the analyte, and the release of the fluorophore. The autonomous release of the fluorophore leads to the amplified optical detection of the analyte. The method is implemented to detect

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...