Highly branched Pt–Ni nanocrystals enclosed by stepped surface for methanol oxidation†
Abstract
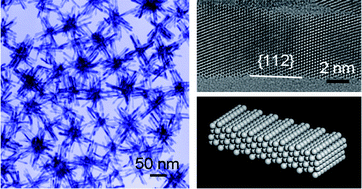
Integrated design of nanocatalysts with a preferential surface atomic arrangement, composition, and overall morphology will provide great opportunities to enhance their catalytic activity and durability. In this work, Pt–Ni bimetallic nanobundles (NBs) with branched morphology and stepped surfaces have been prepared by a seed-based diffusion method. For methanol

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...