High Tg, processable fluorinated polyimides containing benzoisoindoledione unit and evaluation of their gas transport properties
Abstract
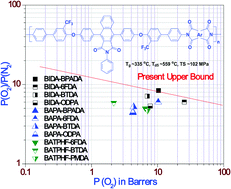
This article describes the preparation of a series of processable fluorinated poly(ether imide)s from a new diamine monomer 4,9-bis-[4-(4′-amino-3-trifluoromethyl-biphenyl-4-yloxy)-phenyl]-2-phenyl-benzo[f]-isoindole-1,3-dione. The polymers showed extremely high Tg (up to 335 °C), outstanding thermal stability (up to 559 °C) and high tensile strength (up to 102 MPa). The transparent (λcut-off ≥ 363 nm) membranes from these polymers were investigated for their gas transport properties for CO2, O2, N2 and CH4 at three different temperatures. The effect of the benzo[f]isoindole-1,3-dione moiety and the aromatic dianhydrides (BPADA, 6FDA, BTDA, ODPA and PMDA) towards the glass transition temperatures of the polymers and their consequences on gas transport properties have been investigated. The polymer prepared from 6FDA showed the highest permeability coefficient for all the gases (PCO2 = 71.3, PO2 = 25.4) whereas BPADA based polymer exhibited the highest permselectivity (CO2/CH4 ∼ 37.2 and O2/N2 ∼ 8.4), staying closer to the latest upper boundary limit drawn by L. M. Robeson.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...