Ketalized poly(amino ester) for stimuli-responsive and biocompatible gene delivery†
Abstract
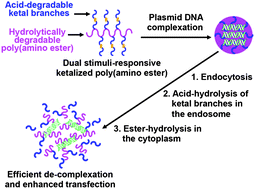
Stimuli-triggered degradation and facilitated intracellular release of nucleic acids are key design factors in developing efficient and biocompatible nonviral gene carriers. In this study, a cationic polymer was developed with aims to achieve enhanced gene transfection and low cytotoxicity via rapid biodegradation and subsequent intracellular de-complexation in response to dual stimuli in a cell. Diaminoethane was polymerized to synthesize cationic and hydrolytically degradable poly(amino ester), and then it was further conjugated with acid-degradable amino ketal branches. The resulting polymer, ketalized poly(amino ester) (K-PAE), differentially degrades via rapid hydrolysis of the ketal branches in the mildly acidic endosome and subsequent gradual degradation of the polyester backbone in the cytoplasm. DNA/K-PAE polyplexes underwent acid-triggered de-complexation at an endosomal pH, leading to efficient intracellular release of DNA and significantly enhanced transfection efficiency. In addition, DNA/K-PAE polyplexes demonstrated low cytotoxicity and serum-resistant gene transfection, in comparison with commercial counterpart polymers, promising for efficient and safe gene delivery in vivo. This study presents insightful design clues for developing efficient, versatile, stimuli-responsive, and biocompatible polymers for nonviral gene delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...