Palladium-containing polymers via a combination of RAFT and triazole chemistry†
Abstract
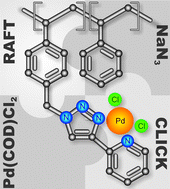
Polystyrene based copolymers with palladium-ligating side groups were obtained by RAFT polymerization of chloromethyl styrene and styrene, subsequent azide transformation and quantitative copper-mediated 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of ethynyl pyridine. Variable copolymer compositions were synthesized ranging from 10% to 50% with respect to the fraction of the palladium-ligating comonomer. The successful loading of the polymers with PdCl2 employing [Pd(COD)Cl2] (COD = 1,5-cyclooctadiene) as the metal source was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and elemental analysis. Absolute molecular weights of the Pd-containing polymers ranging from Mw = 16 000 g mol−1 to 20 000 g mol−1 were determined by employing static light scattering (SLS). In order to fully clarify the incorporation of palladium into the polymers, a PdCl2 complex of a chelating N donor ligand featuring the characteristic heterocyclic donor functions used to incorporate PdCl2 in the polymer was synthesized and characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction and NMR analysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...