Electronically excited states of DNA oligonucleotides with disordered base sequences studied by fluorescence spectroscopy†‡
Abstract
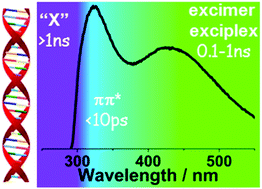
DNA double-stranded oligomers are studied by steady-state and
- This article is part of the themed collection: In honour of Jean-Pierre Desvergne

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...