Binding trimethyllysine and other cationic guests in water with a series of indole-derived hosts: large differences in affinity from subtle changes in structure†
Abstract
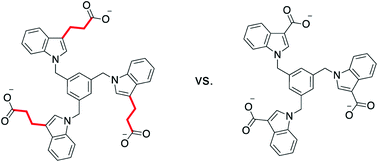
The binding of a series of indole-derived hosts to various ammonium cations in pure, buffered water is investigated using both solution phase 1H NMR studies and computational modeling. These hosts can engage their targets via the cation–pi interaction, electrostatic attraction, and the hydrophobic effect. The hydrophobic effect is shown to be a dominant influence in the strength of the binding interactions, both in terms of the hydrophobicity of the host and of the guest. Our findings show that small changes that reduce the host hydrophobic surface area without reducing either the number of negative charges or amount of aromatic surface area are found to significantly decrease binding. Additionally, the position of solubilizing charges is also shown to influence the preferred host geometry and resulting binding constants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...