Controlled immobilisation of active enzymes on the cowpea mosaic virus capsid†
Abstract
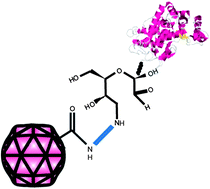
Immobilisation of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and glucose oxidase (GOX) via covalent attachment of modified enzyme carbohydrate to the exterior of the cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV) capsid gave high retention of enzymatic activity. The number of enzymes bound per virus was determined to be about eleven for HRP and 2–3 for GOX. This illustrates that relatively large biomacromolecules can be readily coupled to the virus surface using simple conjugation strategies. Virus-biomacromolecule hybrids have great potential for uses in catalysis, diagnostic assays or biosensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...