A highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor based on zinc oxide nanotetrapods for l-lactic acid detection
Abstract
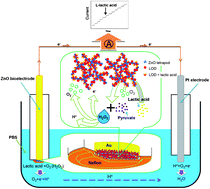
An amperometric biosensor based on zinc oxide (ZnO) nanotetrapods was designed to detect L-lactic acid. The lactate oxidase was immobilized on the surface of ZnO nanotetrapods by electrostatic adsorption. Unlike traditional detectors, the special four-leg individual ZnO nanostructure, as an adsorption layer, provides multiterminal charge transfer channels. Furthermore, a large amount of ZnO tetrapods are randomly stacked to form a three-dimensional network naturally that facilitates the exchange of electrons and ions in the phosphate buffer solution. Utilizing amperometric response measurements, the prepared ZnO nanotetrapod L-lactic acid biosensor displayed a detection limit of 1.2 μM, a low apparent Michaelis–Menten constant of 0.58 mM, a high sensitivity of 28.0 μA cm−2 mM−1 and a good linear relationship in the range of 3.6 μM–0.6 mM for the L-lactic acid detection. This study shows that the biosensor based on ZnO tetrapod nanostructures is highly sensitive and able to respond rapidly in detecting lactic acid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...