Structural and electronic properties of bilayer and trilayer graphdiyne†
Abstract
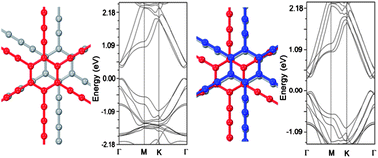
Stimulated by the recent experimental synthesis of a new layered carbon allotrope–graphdiyne film, we provide the first systematic ab initio investigation of the structural and electronic properties of bilayer and trilayer graphdiyne and explore the possibility of tuning the energy gap via a homogeneous perpendicular electric field. Our results show that the most stable bilayer and trilayer graphdiyne both have their hexagonal carbon rings stacked in a Bernal way (AB and ABA style configuration, respectively). Bilayer graphdiyne with the most and the second most stable stacking arrangements have direct bandgaps of 0.35 eV and 0.14 eV, respectively; trilayer graphdiyne with stable stacking styles have bandgaps of 0.18–0.33 eV. The bandgaps of the semiconducting bilayer and trilayer graphdiyne generally decrease with increasing external vertical electric field, irrespective of the stacking style. Therefore, the possibility of tuning the electronic structure and optical absorption of bilayer and trilayer graphdiyne with an external electric field is suggested.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...