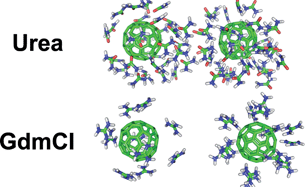
It has been a long history that urea and guanidinium chloride (GdmCl) are used as agents for denaturing proteins. The underlying mechanism has been extensively studied in the past several decades. However, the question regarding why GdmCl is much stronger than urea has seldom been touched. Here, through molecular dynamics simulations, we show that a 4 M GdmCl solution is more able than 7 M urea solution to dissociate both hydrophobic and charged nano-particles (NP). Both urea and GdmCl affect the NPs' aggregation through direct binding to the NP surface. The advantages of GdmCl originate from the net charge of bound guanidinium ions which can generate a local positively charged environment around hydrophobic and negatively charged NPs. This effective coating can introduce Coulombic repulsion between all the NPs. Urea shows certain ability to dissociate hydrophobic NPs. However, in the case of charged NPs, urea molecules located between two opposite-charged NPs will form ordered hydrogen bonds, acting like “glue” which prevents separation of the NPs. Although urea can form hydrogen bonds with either hydrophilic amino acids or the protein backbone, which are believed to contribute to protein denaturation, our findings strongly suggest that this property does not always contribute positively to urea's denaturation power.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...