Experimental and theoretical evaluation of nanodiamonds as pH triggered drug carriers†
Abstract
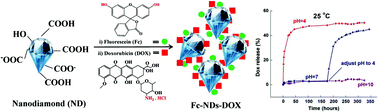
Nanodiamond (ND) and its derivatives have been widely used for
* Corresponding authors
a
Controlled Release and Delivery Lab (CRD), Advanced Membranes and Porous Materials Center, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Thuwal, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
E-mail:
niveen.khashab@kaust.edu.sa
Fax: +966-2-802-1172
Tel: +966-2-808-2410
b Chemical and Life Sciences and Engineering Division, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Thuwal, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
c Université de Bordeaux, IPB-ENSCBP, F-33600 Pessac, France, UMR 5629 F- 33600 Pessac, France
Nanodiamond (ND) and its derivatives have been widely used for

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
J. Yan, Y. Guo, A. Altawashi, B. Moosa, S. Lecommandoux and N. M. Khashab, New J. Chem., 2012, 36, 1479 DOI: 10.1039/C2NJ40226B
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
