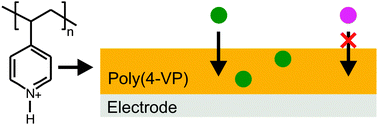
The cathodic electropolymerization conditions for poly(4-vinylpyridine) and the uptake characteristics of anions were evaluated with respect to their application to electrochemical sensing. The membranes were deposited from acidified acetonitrile solutions to minimize hydrogen gas evolution, which is prevalent in aqueous media at the applied potential range. Mid-infrared spectroscopic studies resulted in quantitative data relating the amount of monomer protonated with respect to the added acid, while 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy provided insight into the resonance form preferentially adopted by the protonated monomer. The presence of defects in poly(4-VP) films was indirectly measured by monitoring the obstructed diffusion of cationic redox species through the film, and by correlating these electrochemical studies with mid-infrared spectroscopic analysis it became possible to determine the protonated-to-unprotonated monomer ratio yielding uniformly coated electrodes. Finally, the diffusion of Fe(CN)64− through poly(4-VP)-coated electrodes was evaluated as a function of pH, resulting in the conclusion that, unlike similarly deposited poly(2-VP) membranes, poly(4-VP) does not possess the loading capacity required for pre-concentration of anions.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...