Design and synthesis of anthracene-based bispyridinium amides: anion binding, cell staining and DNA interaction studies†
Abstract
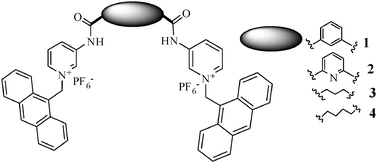
The design and synthesis of anthracene labeled bispyridinium amides 1–4 along with their anion binding, cell staining and DNA interaction studies are reported. All the chemosensors exhibit significant response towards H2PO4− in CH3CN. Furthermore, sensors 2 and 3 are quite interesting for the selective sensing of aliphatic dicarboxylates. Among these compounds, 1 is found to be useful in cell staining. Also all of them exhibit significant interaction with DNA. All these properties are found to be dependent on the nature of the spacer that holds the pyridinium binding sites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...