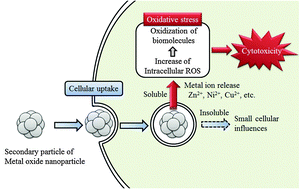
Association of cellular influences and physical and chemical properties were examined for 24 kinds of industrial metal oxide nanoparticles: ZnO, CuO, NiO, Sb2O3, CoO, MoO3, Y2O3, MgO, Gd2O3, SnO2, WO3, ZrO2, Fe2O3, TiO2, CeO2, Al2O3, Bi2O3, La2O3, ITO, and cobalt blue pigments. We prepared a stable medium dispersion for each nanoparticle and examined the influence on cell viability and oxidative stress together with physical and chemical characterizations. ZnO, CuO, NiO, MgO, and WO3 showed a large amount of metal ion release in the culture medium. The cellular influences of these soluble nanoparticles were larger than insoluble nanoparticles. TiO2, SnO2, and CeO2 nanoparticles showed strong protein adsorption ability; however, cellular influences of these nanoparticles were small. The primary particle size and the specific surface area seemed unrelated to cellular influences. Cellular influences of metal oxide nanoparticles depended on the kind and concentrations of released metals in the solution. For insoluble nanoparticles, the adsorption property was involved in cellular influences. The primary particle size and specific surface area of metal oxide nanoparticles did not affect directly cellular influences. In conclusion the most important cytotoxic factor of metal oxide nanoparticles was metal ion release.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...