Chemical synthesis and biological study of 4β-carboxymethyl-epiafzelechin acid, an osteoprotective compound from the rhizomes of Drynaria fortunei†
Abstract
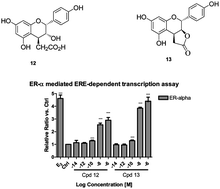
The chemically synthesized active osteoprotective component 12 of Drynaria fortunei (kunze) J. Sm showed potent proliferative activity on UMR-106 osteoblast-like cells and selectively activate ERE-dependent gene transcription mediated by ERα but not ERβ.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...