Estrogen and retinoic acid antagonistically regulate several microRNA genes to control aerobic glycolysis in breast cancer cells†
Abstract
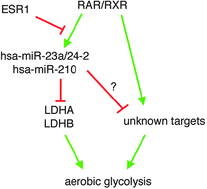
In addition to
* Corresponding authors
a INSERM U896, F-34298Montpellier, France
b Institut de Recherche en Cancérologie de Montpellier, Université Montpellier1, F-34298 Montpellier, France
c Cytoskeleton and Cell Plasticity Laboratory, Life Sciences Research Unit-FSCT, University of Luxembourg, L-1511 Luxembourg, France
d
Institut de Génétique Moléculaire de Montpellier, CNRS UMR 5535 - IFR 122, 1919 Route de Mende, F-34293 Montpellier cedex 5, France
E-mail:
charles.lecellier@igmm.cnrs.fr
Fax: +33 4 67 04 02 31
Tel: +33 4 67 61 36 64
e Université Montpellier 2, Place Eugène Bataillon, F-34095 Montpellier, France
f Université Montpellier 1, 5 Bd Henry IV, F-34967 Montpellier cedex 2, France
g Sanofi, Exploratory Unit, 371, rue du Pr Joseph Blayac, 34184 Montpellier cedex 4, France
h CRLC Val d’Aurelle Paul Lamarque, F-34298 Montpellier, France
In addition to

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
A. Saumet, G. Vetter, M. Bouttier, E. Antoine, C. Roubert, B. Orsetti, C. Theillet and C. Lecellier, Mol. BioSyst., 2012, 8, 3242 DOI: 10.1039/C2MB25298H
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
