Differential Tus–Ter binding and lock formation: implications for DNA replication termination in Escherichia coli†
Abstract
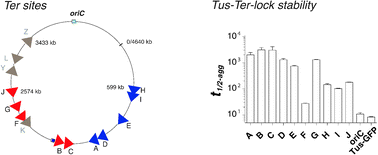
In E. coli, DNA replication termination occurs at Ter sites and is mediated by Tus. Two clusters of five Ter sites are located on each side of the terminus region and constrain replication forks in a polar manner. The polarity is due to the formation of the Tus–Ter-lock intermediate. Recently, it has been shown that DnaB helicase which unwinds DNA at the replication fork is preferentially stopped at the non-permissive face of a Tus–Ter complex without formation of the Tus–Ter-lock and that fork pausing efficiency is sequence dependent, raising two essential questions: Does the affinity of Tus for the different Ter sites correlate with fork pausing efficiency? Is formation of the Tus–Ter-lock the key factor in fork pausing? The combined use of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...