Induced genome maintenance pathways in pre-cancer tissues describe an anti-cancer barrier in tumor development†
Abstract
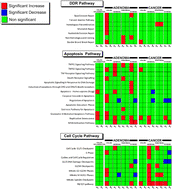
A recent model proposing that a barrier is raised against tumor evolution in pre-cancer tissues is investigated. For that we quantify expression alterations in genome maintenance pathways: DNA damage response, death pathways and cell cycle and also differentially expressed genes in transcriptomes of pre-cancerous and cancerous lesions deposited in the GEO database. We find that the main alterations in pre-cancer samples comprising the barrier are: (1) DNA double strand-breaks signaling and repair pathways induction, (2) upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinases, (3) p53 dependent (and independent) repair and apoptosis pathways induction and (4) replicative senescence induction early in tissue transformation. In the cancer samples we find that the induced pathways in pre-cancer are systematically inhibited and the only remaining induced pathway is p53, whereas the retinoblastoma pathway arises induced in most samples. The results give support to the model, furthermore they reveal the involvement of additional mechanisms in pre-cancer, including the early induction of replicative senescence and of p53 independent apoptosis.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...