Structural and thermodynamic characterization of the self-adhesive properties of human P-cadherin†
Abstract
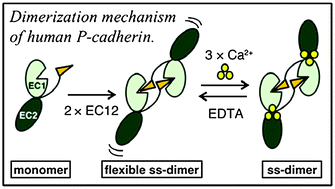
Human P-cadherin is a promising therapeutic target against cancer. However, its characterization at the molecular level is still lacking. We report that human P-cadherin associated irreversibly in a distinct dimer configuration. Unexpectedly, the divalent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...