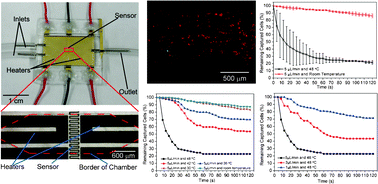
Isolation of cells from heterogeneous mixtures is critically important in both basic cell biology studies and clinical diagnostics. Cell isolation can be realized based on physical properties such as size, density and electrical properties. Alternatively, affinity binding of target cells by surface-immobilized ligands, such as antibodies, can be used to achieve specific cell isolation. Microfluidics technology has recently been used in conjunction with antibody-based affinity isolation methods to capture, purify and isolate cells with higher yield rates, better efficiencies and lower costs. However, a method that allows easy release and collection of live cells from affinity surfaces for subsequent analysis and detection has yet to be developed. This paper presents a microfluidic device that not only achieves specific affinity capture and enrichment, but also enables non-destructive, temperature-mediated release and retrieval of cells. Specific cell capture is achieved using surface-immobilized aptamers in a microchamber. Release of the captured cells is realized by a moderate temperature change, effected via integrated heaters and a temperature sensor, to reversibly disrupt the cell-aptamer interaction. Experimental results with CCRF-CEM cells have demonstrated that the device is capable of specific capture and temperature-mediated release of cells, that the released cells remain viable and that the aptamer-functionalized surface is regenerable.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...