A three-dimensional microvascular gas exchange unit for carbon dioxide capture†
Abstract
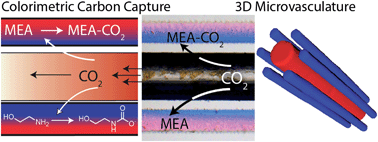
For the capture of CO2 from mixed gas streams, materials for increased gas exchange are necessary. Efficient gas exchange systems already exist in the form of vascularized lung-tissue. Herein we report a fabrication technique for the synthesis of three-dimensional microvascular gas exchange units capable of removing CO2 from flowing gas created using the recently reported Vaporization of a Sacrificial Component (VaSC) technique. We demonstrate the spatiotemporal pattern of CO2 reactivity in the microvascular gas exchange unit using colorimetric, pH sensitive

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...