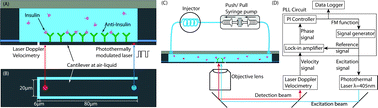
Here we describe the application of a recently developed high-resolution microcantilever biosensor resonating at the air–liquid interface for the continuous detection of antigen–antibody and enzyme–substrate interactions. The cantilever at the air–liquid interface demonstrated 50% higher quality factor and a 5.7-fold increase in signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) compared with one immersed in the purified water. First, a label-free detection of a low molecular weight protein (insulin, 5.8 kDa) in physiological concentration was demonstrated. The liquid facing side of the cantilever was functionalized by coating its surface with insulin antibodies, while the opposite side was exposed to air. The meniscus membrane at the micro-slit around the cantilever sustained the liquid in the microchannel. After optimizing the process of surface functionalization, the resonance frequency shift was successfully measured for insulin solutions of 0.4, 2.0, and 6.3 ng ml−1. To demonstrate additional application of the device for monitoring enzymatic protein degradation, the liquid facing microcantilever surface was coated with human recombinant SOD1 (superoxide dismutase 1) and exposed to various concentrations of proteinase K solution, and the kinetics of the SOD1 digestion was continuously monitored. The results showed that it is a suitable tool for sensitive protein detection and analysis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...