First principles calculations of solid–solid interfaces: an application to conversion materials for lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
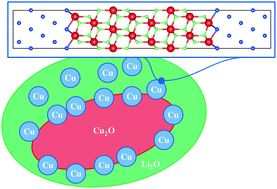
Using periodic density functional theory approaches, the thermodynamic stability of solid–solid interfaces generated during the conversion reaction of copper oxide which is a promising electrode material is investigated. Previous experimental results showed that conversion reactions generate a huge proportion of solid–solid interfaces among Cu2O–Cu, Li2O–Cu and Cu2O–Li2O. Interface grand potentials as a function of the voltage against Li|Li+ were computed in order to determine the chemical composition of the most stable interfaces. Then a structural model of the electrode material is proposed, based on the works of adhesion of the most stable systems identified in the first step.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...