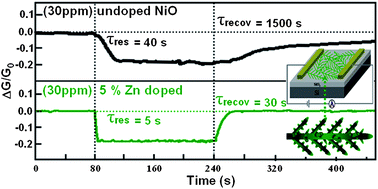
Nanoscale Zn-doped NiO dendritic crystals with a Christmas-tree-like structure, have been successfully synthesized via an electrolytic approach combined with subsequent high temperature oxidation. The trunks have lengths in the range 6–10 μm with diameters varying from 190 nm to 200 nm, and the branches have lengths in the range 1–3 μm with diameters varying from 150 nm to 180 nm. Microstructure characterization indicated that the solubility limit of zinc ions in the NiO lattice sites was lower than 7 mol%. We systematically investigated the gas sensing properties of the Zn-doped NiO sensors for NH3 gas detection at room temperature. The sensor with doped NiO dendritic crystals gave 5–8 times faster responses and 30–50 times faster recovery speeds than the sensor with pristine NiO dendritic crystals, which is important for the practical application of this NiO sensor. The fast response and recovery speeds could be attributed to the effective electron transfer between the doped NiO dendritic crystal networks and the ammonia molecules. Moreover, we found that the doped NiO sensors have excellent reproducibility, reversibility, stability and selectivity toward NH3 gas over other organic gases. Lastly, a possible gas sensing mechanism of NiO dendritic crystal sensors was discussed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...