Temperature-dependent conductive composites: poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-methylol acrylamide) and carbon black composite films
Abstract
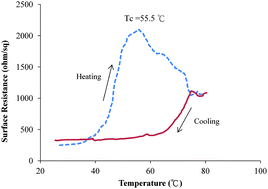
Innovative temperature-dependent conductive composite materials, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-methylol acrylamide)/acid-treated carbon black, poly(NIPAAm-co-NMA)/CB, were prepared. The copolymer of NIPAAm and NMA was synthesized via a random redox copolymerization, and the poly(NIPAAm-co-NMA) copolymer showed thermo-responsive properties. Here, NMA performed a thermal crosslinking function in the copolymer. Carbon black was acid-treated for good dispersion in an aqueous solution. Poly(NIPAAm-co-NMA)/CB composites were obtained by blending various amounts of acid-treated CB into the poly(NIPAAm-co-NMA) aqueous solution, and the films were then post-cured for thermal crosslinking. The properties of the conductive poly(NIPAAm-co-NMA)/CB films such as thermal crosslinking performance, surface resistance, and morphology of the crosslinked composites were investigated. This study demonstrated that the poly(NIPAAm-co-NMA)/CB composites exhibited both temperature-dependent electric resistance and reproducible thermally responsive characteristics. The composites can potentially be applied as new electrical temperature sensor materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...