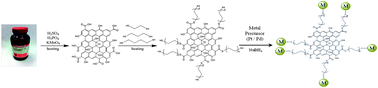
This paper reports the chemical synthesis and experimental characterization of various graphene oxide (GO)-supported platinum (Pt) and palladium (Pd) nanoparticle (NP) catalysts. To investigate the relationship between the linker length and the catalytic activities of the metal-decorated GO catalysts, six samples were prepared with three different linker molecules, HS(CH2)2SH, HS(CH2)3SH and HS(CH2)4SH (denoted as GO-l-NPs), and two different metal NPs, Pt and Pd. All GO-l-NP catalysts were tested in oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) using electrochemical techniques such as cyclic voltammetry (CV) and rotating ring disk electrode (RRDE) hydrodynamic voltammetry to quantitatively obtain the ORR kinetic constants and the reaction mechanisms on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. All GO-l-NPs/GCE electrodes showed significantly improved ORR activity and mechanisms. GO-l-NPs were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The results showed that Pt and Pd were successfully attached onto the GO surface. A more positive potential catalytic ORR was observed in the modified GO-l-NPs with longer chain linker lengths in both cases.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...