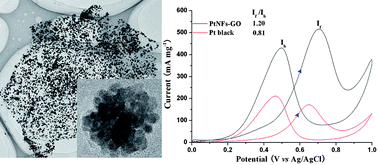
This paper reports a nontoxic, rapid, one-pot and template-free synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) Pt nanoflowers (PtNFs) with high yield and good size monodispersity supported on graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets. The key synthesis strategy employed a low-cost, green solvent, ethanol as the reductant and an advanced, powerful 2D carbon material, GO nanosheets as the stabilizing material. The resulting PtNFs-GO nanosheets were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), high-resolution TEM, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and electrochemical techniques. It was found that the monodispersed, porous PtNFs supported on GO nanosheets were a uniform size of 30 nm and each was composed of numerous “clean” and small (4 nm) Pt nanoparticles, which revealed an unusually high activity for methanol oxidation reaction compared to commercial Pt black. Furthermore, based on a systematic study of the PtNFs growth conditions, a possible mechanism, and especially the importance of GO in the formation was proposed. Our study demonstrates that GO is a promising support material for developing next-generation advanced Pt based fuel cells and their relevant electrodes in the field of energy.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...