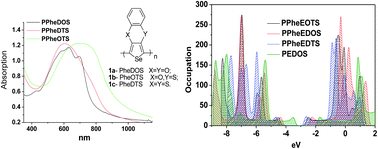
In this work, we prepared a series of new conjugated polyselenophenes that, in the 3,4-positions of the selenophene ring, have oxygen or sulfur substituents bridged by a phenylene moiety. Such substitution of a conjugated backbone produces a skeleton that has only planar units, does not have stereo centers, and offers the potential to structurally modify the polymer without impairing its conjugation. The reported polyselenophenes exhibit significantly different properties as a function of the heteroatom. The selenophene backbone combined with a phenylene periphery creates the rare combination of a low-band gap, low HOMO energy level, and a flat skeleton, which is desired for many optoelectronic applications. The properties of the phenylene-bridged polyselenophenes were compared with those of their polythiophene analogs. The polyselenophenes obtained in this work have a lower band gap and higher planarity than polythiophenes and their monomers electropolymerize more easily. Theoretical studies support the experimental findings about rigidity and band gap changes.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...