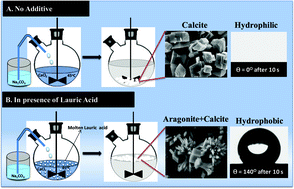
This paper demonstrates a novel method for the in situ surface modification (from hydrophilic to hydrophobic/oleophilic) and phase selectivity of aragonite over calcite, induced by molten lauric acid, through a one-step, solvent-free route. The final product is extremely hydrophobic and is easy to isolate. While in the absence of lauric acid, formation of hydrophilic rhombohedral calcite particles is observed, lauric acid as an additive leads to the formation of hydrophobic CaCO3 particles comprising of rosette-shaped aragonite as the predominant phase. In addition, increase in concentration of lauric acid increases the water contact angle gradually to 140°. Powder X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy confirm the phase and morphology of different CaCO3 particles, respectively. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermo-gravimetric analysis establish the presence of calcium laurate in the hydrophobic CaCO3 samples. Water contact angle measurements demonstrate the extent of surface hydrophobicity. Moreover, the hydrophobic CaCO3 particles show selective absorption of oil from an oil–water mixture. Thus, the current method of in situ synthesis of hydrophobic CaCO3 particles may provide an environmentally friendly, cost-efficient technology to clean up catastrophic oil spills.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...