A general chiral selector immobilized on silica magnetic microspheres for direct separation of racemates†
Abstract
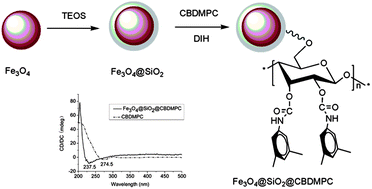
Magnetic nanoparticles modified by specific ligands have been widely applied in various fields in terms of its magnetic property. Chiral discrimination of racemates into enantiomers is a very challenging task because of their identical physical and chemical properties. It is recognized that nanoparticles composed of magnetic cores with chiral ligands on its surface simultaneously possess both magnetic property and chiral recognition ability. Therefore, developing a general chiral magnetic material is the most important target in this paper. Cellulose-2,3-bis(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) (CBDMPC), as one of the most effective chiral stationary phases in HPLC, was chosen to be immobilized onto the surface of silica-coated magnetite to form chiral magnetic microsphere Fe3O4@SiO2@CBDMPC (CMM). Then, the successful immobilization of CBDMPC onto the surface of silica-coated microspheres was confirmed by infrared spectra and circular dichroism spectra. Finally, direct separation of enantiomers involving the application of the magnetic nanomaterial was introduced into the field of chiral separation. The separation results suggested that CMM displayed chiral recognition ability to different kinds of racemates, which demonstrated its feasibility to be a potential material for chiral separation. In addition, an external magnetic field made the recycling of CMM quite convenient.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...