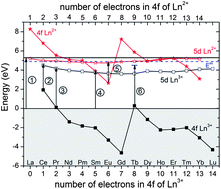
RE3+ (RE = Pr, Sm, Tb, Tb/Ce)-activated CaAlSiN3 samples were prepared by a solid-state reaction method at high temperature, and their photoluminescence properties were investigated. An interesting observation is that the 5d bands of Pr3+ and Tb3+ are at rather low energy in CaAlSiN3 compared to oxides. Pr3+-doped CaAlSiN3 shows strong 4f15d1 → 4f2 emission bands (334–480 nm) as well as typical 4f2 → 4f2 emission lines (480–800 nm) of Pr3+ under 4f2 → 4f15d1 excitation. Sm3+-doped CaAlSiN3 exhibits bright red emission originating from 4G5/2 → 6HJ (J = 5/2, 7/2 and 9/2) transitions, and the charge transfer band of Sm3+ was observed at an unusually low energy of 3.91 eV. In Tb3+-doped samples, the direct Tb3+ 4f8 → 4f75d1 excitation leads to 5D3 → 7FJ (J = 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1) (blue) and 5D4 → 7FJ (J = 6, 5, 4, 3) (green) line emissions. The bands at about 252 nm in the excitation spectra are attributed to the host lattice absorption. It is observed that there is energy transfer from the host lattice to the luminescent activators (Pr3+, Sm3+, Tb3+). In Tb3+/Ce3+-codoped CaAlSiN3, an effective energy transfer process exists from Tb3+ to Ce3+. A detailed energy level diagram that contains the position of the 4f and 5d levels of all divalent and trivalent lanthanide ions with respect to the valence and conduction bands of CaAlSiN3 has been constructed and explained.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...