Rationally designed functional macroporous materials as new adsorbents for efficient phosphorus removal†
Abstract
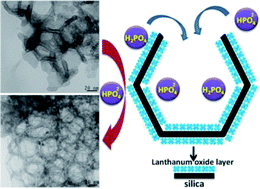
Novel phosphorus (P) adsorbents with a high adsorption capacity (up to 2.272 mmol g−1) and excellent
* Corresponding authors
a
ARC Centre of Excellence for Functional Nanomaterials, Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
E-mail:
c.yu@uq.edu.au
Fax: +61 7-334 63973
b State Key Laboratory of Heavy Oil Processing, China University of Petroleum, No. 18 Fuxue Rd, Beijing 102249, China
c Materials Engineering and Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
d Advanced Water Management Centre (AWMC), The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Novel phosphorus (P) adsorbents with a high adsorption capacity (up to 2.272 mmol g−1) and excellent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
J. Yang, P. Yuan, H. Chen, J. Zou, Z. Yuan and C. Yu, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 9983 DOI: 10.1039/C2JM16681J
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
