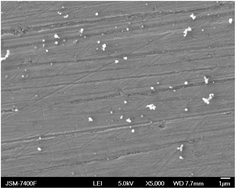
Carbon nanomaterials have become increasingly important for many applications, including sensors, electronics, biomedical materials and functional composites. Currently their production is based on hydrocarbons or graphite and requires very high temperatures. Here we present a method for the synthesis of carbon nanomaterials from carbon dioxide. Unlike previously described methods, our synthesis method works near room temperature. Carbon dioxide is irradiated at its critical point, producing spherical carbon nanoparticles even without the use of a catalyst. We examine the influence of irradiation parameters and different metals and catalysts on the nanocarbon production. Together with analysis of the fluid phase, this allows us to draw some conclusions on the carbon dioxide dissociation mechanism.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...