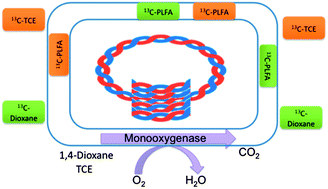
An intrinsic biodegradation study involving the design and implementation of innovative environmental diagnostic tools was conducted to evaluate whether monitored natural attenuation (MNA) could be considered as part of the remedial strategy to treat an aerobic aquifer contaminated with 1,4-dioxane and trichloroethene (TCE). In this study, advanced molecular biological and stable isotopic tools were applied to confirm in situ intrinsic biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane and TCE. Analyses of Bio-Trap® samplers and groundwater samples collected from monitoring wells verified the abundance of bacteria and enzymes capable of aerobically degrading TCE and 1,4-dioxane. Furthermore, phospholipid fatty acid analysis with stable isotope probes (PLFA-SIP) of the microbial community validated the ability for microbial degradation of TCE and 1,4-dioxane. Compound specific isotope analysis (CSIA) of groundwater samples for TCE resulted in δ13C values that indicated likely biodegradation of TCE in three of the four monitoring wells sampled. Results of the MNA evaluation showed that enzymes capable of aerobically degrading TCE and 1,4-dioxane were present, abundant, and active in the aquifer. Taken together, these results provide direct evidence of the occurrence of TCE and 1,4-dioxane biodegradation at the study site, supporting the selection of MNA as part of the final remedy at some point in the future.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...