Fragmentation of extracellular DNA by long-term exposure to radiation from uranium in aquatic environments
Abstract
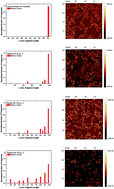
Persistent harmful scenarios associated with disposal of radioactive waste, high-background radiation areas and severe nuclear accidents are of great concern regarding consequences to both human health and the environment. Of particular concern is the extracellular DNA in aquatic environments contaminated by radiological substances. Strand breaks induced by radiation promote decrease in the transformation efficiency for extracellular DNA. The focus of this study is the quantification of DNA damage following long-term exposure (over one year) to low doses of natural uranium (an alpha particle emitter) to simulate natural conditions, since nothing is known about alpha radiation induced damage to extracellular DNA. A high-resolution

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...