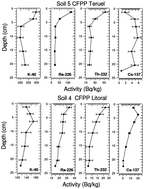
The production of electricity in coal-fired power plants (CFPP) is considered a NORM (Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials) activity because the coals they burn can present relatively high contents of the naturally occurring radionuclides. In this study, the main radiological impact pathways into the surrounding environments of the four largest coal-fired power plants in Spain were analyzed. These pathways are, first, atmospheric evacuations and wind resuspension and, second, effluent evacuations to nearby rivers or directly to the sea. The atmospheric releases of radionuclides were evaluated by the analyses of soil profiles in the vicinities of the CFPPs. No significant enhancement of radionuclides in the surface soil was observed at the points of maximum deposition of combustion gases, located from 4.3 to 13 km away depending on the considered CFPP. However, an increase of 40K, 226Ra, and 232Th in the surface soils was observed in the first kilometre from the chimney for two CFPPs. This suggested that these radionuclides were released in particulate form. There was also a net influence of the climate in which the CFPPs were located. This was observed in the two CFPPs that were in dry environments, while no increase was observed in the other two, located in more humid environments. The liquid effluents released usually presented an enhancement of dissolved chemical species regarding the initial intake water. Enrichments of the 234,238U and 226Ra contents in the water used in the plants' routine procedures were observed, and of 210Po in the wastewater of just one of the plants. In any case, this enhancement was below the parametric value for the Total Indicative Dose for the hypothetical human consumption of the released waters. As a consequence of these releases of radionuclides, local products destined for human consumption produced in the vicinity of the facilities might incorporate natural radionuclides by these pathways, finding no significant enhancement of the natural radionuclide contents due to the CFPPs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...