Oxygen electrocatalysts for water electrolyzers and reversible fuel cells: status and perspective†
Abstract
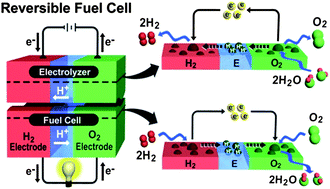
Hydrogen production by electrochemical water electrolysis has received great attention as an alternative technology for energy conversion and storage. The oxygen electrode has a substantial effect on the performance and durability of water electrolyzers and reversible (or regenerative) fuel cells because of its intrinsically slow kinetics for oxygen evolution/reduction and poor durability under harsh operating environments. To improve oxygen kinetics and durability of the electrode, extensive studies for highly active and stable oxygen electrocatalysts have been performed. However, due to the thermodynamic instability of transition metals in acidic media, noble metal compounds have been primarily utilized as electrocatalysts in water electrolyzers and reversible fuel cells. For water electrolyzer applications, single noble metal oxides such as ruthenium oxide and iridium oxide have been studied, and binary or ternary metal oxides have been developed to obtain synergistic effects of each component. On the other hand, a variety of bifunctional electrocatalysts with a combination of monofunctional electrocatalysts such as platinum for oxygen reduction and iridium oxide for oxygen evolution for reversible fuel cell applications have been mainly proposed. Practically, supported iridium oxide-on-platinum, its reverse type, and non-precious metal-supported platinum and iridium bifunctional electrocatalysts have been developed. Recent theoretical calculations and experimental studies in terms of water electrolysis and fuel cell technology suggest the effective ways to cope with current major challenges of cost and durability of oxygen electrocatalysts for technical applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Catalysis for Clean Energy

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...