DNA targeting polyaza macrobicyclic dizinc(ii) complexes promoting high in vitro caspase dependent anti-proliferative activity against human carcinoma cancer cells†
Abstract
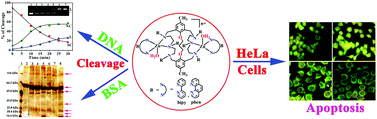
A series of macrobicyclic dizinc(II) complexes [Zn2L1–2B](ClO4)4 (1–6) have been synthesized and characterized (L1–2 are polyaza macrobicyclic binucleating ligands, and B is the N,N-donor heterocyclic base (viz. 2,2′-bipyridine (bipy) and 1,10-phenanthroline (phen)). The DNA and protein binding, DNA hydrolysis and anticancer activity of these complexes were investigated. The interactions of complexes 1–6 with calf thymus DNA were studied by spectroscopic techniques, including absorption, fluorescence and CD spectroscopy. The DNA binding constant values of the complexes were found to range from 2.80 × 105 to 5.25 × 105 M−1, and the binding affinities are in the following order: 3 > 6 > 2 > 5 > 1 > 4. All the dizinc(II) complexes 1–6 are found to effectively promote the hydrolytic cleavage of plasmid pBR322 DNA under anaerobic and aerobic conditions. Kinetic data for DNA hydrolysis promoted by 3 and 6 under physiological conditions give observed rate constants (kobs) of 5.56 ± 0.1 and 5.12 ± 0.2 h−1, respectively, showing a 107-fold rate acceleration over the uncatalyzed reaction of dsDNA. Remarkably, the macrobicyclic dizinc(II) complexes 1–6 bind and cleave bovine serum albumin (BSA), and effectively promote the caspase-3 and caspase-9 dependent deaths of HeLa and BeWo cancer cells. The cytotoxicity of the complexes was further confirmed by lactate dehydrogenase enzyme levels in cancer cell lysate and content media.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...